배움 저장소
[Data Structures] 챕터3. 배열 본문
문자열 ADT
Data Type : 저장공간의 크기, 같은 Data Type의 연산을 정의한다.
Abstract Data Type
- 구현 하지 않은 Data Type.
- 어떤 일을 해야하는 지 정의되어 있다.
예)
class MyString
{
public:
MyString(); // 비어 있는 MyString() 생성
MyString(const char* init); // 맨 뒤에 널 캐릭터'\0'가 들어 있는 문자열로부터 초기화
MyString(const MyString& str); // MyString의 다른 instance로부터 초기화
~MyString();
bool IsEmpty();
bool IsEqual(const MyString& str);
int Length();
void Resize(int new_size);
MyString Substr(int start, int num); // 인덱스 start위치의 글자부터 num개의 글자로 새로운 문자열 만들기
MyString Concat(MyString app_str); // 뒤에 덧붙인 새로운 문자열 반환 (append)
MyString Insert(MyString t, int start); // 중간에 삽입
int Find(MyString pat);
void Print();
private:
char* str_ = nullptr; // 마지막에 '\0' 없음
int size_ = 0; // 글자 수
};
문자 배열 값을 복사할 때 for 반복문 대신 memcpy를 활용할 수 있다.
// 데이터 복사
for (int i = 0; i < size_; ++i)
str_[i] = init[i];
// 데이터 복사
memcpy(str_, init, size_);
복사생성자
MyString::MyString(const MyString& str)
{
// 기본 복사생성자는 포인터주소만 복사, 소멸시 오류
size_ = str.size_;
str_ = new char[size_];
memcpy(str_, str.str_, size_);
}
동적할당 메모리 해제
메모리 할당이 되어있지 않을 때 메모리를 해제하면 에러가 발생한다.
if (str_ != nullptr)
{
delete[] str_;
str_ = nullptr;
size_ = 0;
}
Resize
void MyString::Resize(int new_size)
{
if (new_size != size_)
{
...
}
}주의
동적할당 메모리를 재할당할 때 기존의 메모리를 반드시 반환해주자.
Concat
MyString MyString::Concat(MyString app_str)
{
MyString temp;
temp.Resize(size_ + app_str.size_);
for (int i = 0; i < size_; ++i)
temp.str_[i] = str_[i];
for (int i = 0; i < app_str.size_; ++i)
temp.str_[size_ + i] = app_str.str_[i];
return temp;
}
for (int i = 0; i < app_str.size_; ++i)
temp.str_[size_ + i] = app_str.str_[i];memcpy를 활용하여 배열 포인터의 중간 index부터 복사하기
memcpy(temp.str_ + size_, app_str.str_, app_str.size_);
// or
memcpy(&temp.str_[size_], app_str.str_, app_str.size_);
Find
내 구현
int MyString::Find(MyString pat)
{
for (int i = 0; i < size_; ++i)
{
if (str_[i] == pat.str_[0])
{
bool isEqual = true;
for (int j = 0; j < pat.size_; ++j)
{
if (str_[i + j] != pat.str_[j])
{
isEqual = false;
break;
}
}
if (isEqual)
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
우수 풀이
int MyString::Find(MyString pat)
{
// "ABC" 에서 "DE"를 찾는다면
// ^ 위치에서 더 찾을 필요가 없다
// 글자 개수가 X라면 마지막 글자부터 X-1번째는 확인하지 않아도 됨
for (int start = 0; start <= Length() - pat.Length(); ++start)
{
for (int j = 0; j < pat.size_; ++j)
{
if (str_[start + j] != pat.str_[j])
break;
if (j == pat.Length() - 1)
return start;
}
}
return -1;
}
더 빠른 풀이
Knuth-Morris-Pratt
Find의 최악의 시간복잡도
원본 문자열의 길이가 n이고 찾으려는 문자열의 길이가 n일 때 시간복잡도를 계산한다.
2중 for루프만 보면 O( (m-n+1) * n )이다. 이 때 m이 n보다 크면 O(mn)
다항식
Eval
다항식 2x^2 = 2 * pow(x,2)
float Polynomial::Eval(float x)
{
float temp = 0.0f;
// 힌트 std::powf(2.0f, float(3)); // 2.0f^3.0f = 8.0f (2.0f의 3.0f 제곱)
for (int i = 0; i < capacity_; ++i)
{
if (coeffs_[i] != 0)
temp += coeffs_[i] * powf(x, (float)i);
}
return temp;
}이 때 i는 integer 자료형이므로 float로 형변환해주자
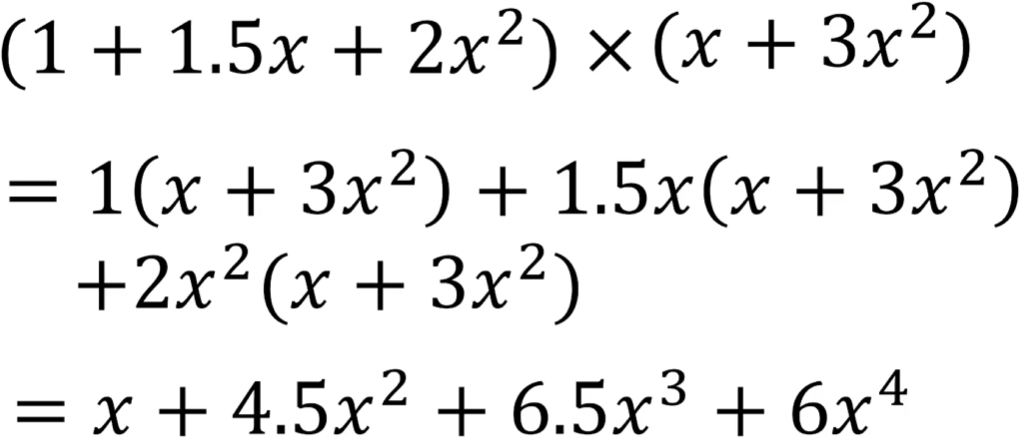
두 다항식의 곱은 다음과 같은 방법으로도 구할 수 있다.
1. 두 다항식의 요소를 각각 하나씩 조합하여 모든 경우를 나열한다.
2. 각 조합의 내부 원소를 모두 곱한 뒤 총합하면 두 다항식의 곱이된다.
Polynomial Polynomial::Mult(const Polynomial& poly)
{
assert(poly.capacity_ == this->capacity_); // 문제를 단순화하기 위한 가정
Polynomial temp(this->MaxDegree());
for (int i = 0; i < poly.capacity_; ++i)
{
if (poly.coeffs_[i] == 0)
continue;
for (int j = 0; j < this->capacity_; ++j)
{
if (this->coeffs_[j] == 0)
continue;
if(i+j < MaxDegree())
temp.coeffs_[i+j] += poly.coeffs_[i] * this->coeffs_[j];
}
}
return temp;
}
희소다항식(Sparse Polynomial)
계수가 0인 항이 많은 다항식을 희소다항식(Sparse Polynomial)이라 한다
위에서 구현한 다항식은 최대 차수항을 기준으로 메모리 공간을 사용한다.
희소다항식은 꼭 필요한 차수항만 데이터를 저장한다.
struct Term
{
float coef;
int exp;
};
class SparsePolynomial
{
private:
Term* terms_ = nullptr;
};높은 차수를 가지고 있지만 항의 개수가 적은 경우 그냥 다항식보다 빠르다
구현방법
A 다항식과 B 다항식을 더하여 C 다항식을 만든다. 이 때 두 다항식 모두 차수항이 정렬되어있다.
index를 사용하여 차수항이 낮은 쪽을 C 다항식에 밀어넣는다.
차수항이 동일할 때 합한 값을 C 다항식에 밀어넣는다.
내구현
SparsePolynomial SparsePolynomial::Add(const SparsePolynomial& poly)
{
SparsePolynomial temp;
int polyIdx = 0;
int thisIdx = 0;
while (true)
{
int thisExp = this->terms_[thisIdx].exp;
int polyExp = poly.terms_[polyIdx].exp;
if (polyIdx < poly.num_terms_ && thisIdx < this->num_terms_)
{
if (thisExp == polyExp)
{
float sumCoef = poly.terms_[polyIdx].coef + this->terms_[thisIdx].coef;
temp.NewTerm(sumCoef, polyExp);
thisIdx++;
polyIdx++;
}
else if (thisExp > polyExp)
{
temp.NewTerm(poly.terms_[polyIdx].coef, polyExp);
polyIdx++;
}
else if (thisExp < polyExp)
{
temp.NewTerm(this->terms_[thisIdx].coef, thisExp);
thisIdx++;
}
}
else if (polyIdx < poly.num_terms_)
{
temp.NewTerm(poly.terms_[polyIdx].coef, polyExp);
polyIdx++;
}
else if (thisIdx < this->num_terms_)
{
temp.NewTerm(this->terms_[thisIdx].coef, thisExp);
thisIdx++;
}
else
{
break;
}
}
return temp;
}
우수구현
SparsePolynomial SparsePolynomial::Add(const SparsePolynomial& poly)
{
SparsePolynomial temp;
int i = 0, j = 0;
while ((i < this->num_terms_) && (j < poly.num_terms_))
{
if ((terms_[i].exp == poly.terms_[j].exp))
{
float sum = poly.terms_[j].coef + terms_[i].coef;
if (sum != 0.f)
temp.NewTerm(sum, terms_[i].exp);
++i;
++j;
}
else if ((terms_[i].exp > poly.terms_[j].exp))
{
temp.NewTerm(poly.terms_[j].coef, poly.terms_[j].exp);
++j;
}
else
{
temp.NewTerm(terms_[i].coef, terms_[i].exp);
++i;
}
}
// i가 끝날 경우 실행되지 않음
for (; i < num_terms_; i++)
temp.NewTerm(terms_[i].coef, terms_[i].exp);
// j가 끝날 경우 실행되지 않음
for (; j < poly.num_terms_; j++)
temp.NewTerm(poly.terms_[j].coef, poly.terms_[j].exp);
return temp;
}
시간복잡도
알고리즘의 시간복잡도는 O(m+n)
이 때 메모리를 동적할당 할 때 필요한 시간복잡도는 O( log2(N) )
예) 2^5를 가정할 때 0 - 1 - 2 - 4 - 8 - 16 - 32
메모리 크기를 100을 할당받을 때와 10000을 할당받을 때의 속도는 동일하다. 따라서 N개의
void SparsePolynomial::NewTerm(float coef, int exp)
{
...
if (num_terms_ >= capacity_)
{
capacity_ = capacity_ > 0 ? capacity_ * 2 : 1; // 2배씩 증가
Term* new_term = new Term[capacity_];
...
}
...
}
행렬
1차원 배열을 활용하여 2차원 배열처럼 사용할 수 있다.
참고 const
함수 안에서 멤버 변수의 값을 바꾸지 않겠다는 의미
float Matrix::GetValue(int row, int col) const;
Transpose
내구현
Matrix Matrix::Transpose()
{
Matrix temp(num_cols_, num_rows_); // num_cols_, num_rows_ 순서 주의
for (int i = 0; i < num_cols_ * num_rows_; ++i)
{
int row = i / num_cols_;
int col = i % num_cols_;
temp.SetValue(col, row, this->GetValue(row, col));
}
return temp;
}
참고 구현
Matrix Matrix::Transpose()
{
Matrix temp(num_cols_, num_rows_); // num_cols_, num_rows_ 순서 주의
for (int r = 0; r < num_rows_; ++r)
for (int c = 0; c < num_cols_; ++c)
temp.SetValue(c, r, GetValue(r, c));
return temp;
}
Add
내구현
Matrix Matrix::Add(const Matrix& b)
{
assert(b.num_cols_ == num_cols_);
assert(b.num_rows_ == num_rows_);
Matrix temp(num_rows_, num_cols_);
for (int i = 0; i < num_rows_ * num_cols_; ++i)
temp.values_[i] = b.values_[i] + this->values_[i];
return temp;
}
참고구현
Matrix Matrix::Add(const Matrix& b)
{
assert(b.num_cols_ == num_cols_);
assert(b.num_rows_ == num_rows_);
Matrix temp(num_rows_, num_cols_);
for (int r = 0; r < num_rows_; ++r)
for (int c = 0; c < num_cols_; ++c)
temp.SetValue(r, c, GetValue(r, c) + b.GetValue(r, c));
return temp;
}
동적 배열의 배열
1. 동적할당으로 포인터 배열을 만든다.
2. 이 때 각 포인터는 동적할당 배열을 가리킨다.
1차원 배열로 2차원 배열처럼 사용 VS 동적할당 포인터 배열을 활용
1차원 배열
아주 큰 저장공간을 OS에게 요구할 경우 연속되지 않은 메모리를 할당받을 수 있다.
동적할당 포인터 배열
각 Row 별로 나누어 저장할 수 있다.
동적할당 포인터 배열의 크기만큼 추가적인 저장공간을 차지한다.
복사생성자 구현
Array2D::Array2D(const Array2D& b)
{
this->num_rows_ = b.num_rows_;
this->num_cols_ = b.num_cols_;
arrays_ = new float* [b.num_rows_];
for (int r = 0; r < b.num_rows_; ++r)
{
arrays_[r] = new float[b.num_cols_];
for (int c = 0; c < b.num_cols_; ++c)
arrays_[r][c] = b.arrays_[r][c];
}
}
Array2D::Array2D(const Array2D& b)
{
this->num_rows_ = b.num_rows_;
this->num_cols_ = b.num_cols_;
arrays_ = new float* [b.num_rows_];
for (int r = 0; r < b.num_rows_; ++r)
{
arrays_[r] = new float[b.num_cols_];
memcpy(arrays_[r], b.arrays_[r], sizeof(float) * num_cols_);
}
}
C++ 정적 2차원 배열
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int arr[3][2] = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6}; // 2차원 (정적) 배열
for(int j = 0; j < 3; j ++)
for(int i = 0; i < 2; i ++)
cout << arr[j][i] << " "; // <- 정적 2차원 배열도 2차원 인덱싱 가능
return 0;
}
희소 행렬(Sparse Matrix)
전체에서 값이 0인 항의 비중이 큰 행렬을 희소행렬(Sparse Matrix)라 한다.
희소행렬은 값이 0인 항을 저장하지 않는다.
0이 아닌 값을 가지는 항이 정렬되게 구현하자.
내구현
void SparseMatrix::SetValue(int row, int col, float value)
{
if (value == 0.0f) return; // value가 0이 아닌 term만 저장
int i;
for (i = 0; i < num_terms_; ++i)
{
if (row < terms_[i].row)
{
break; // row를 기준으로 새로 넣을 위치를 찾음
}
else if (row == terms_[i].row)
{
for (; i < num_terms_; ++i)
{
if (row < terms_[i].row)
break; // i를 높였을 때 row가 변했다면 해당 위치에 넣기
if (col <= terms_[i].col )
break; // row가 일정할 때 col을 기준으로 위치 찾기
}
break;
}
}
// Shift
if (col != terms_[i].col)
for (int j = num_terms_ - 1; i < j; --j)
terms_[j] = terms_[j - 1];
MatrixTerm NewTerm;
NewTerm.col = col;
NewTerm.row = row;
NewTerm.value = value;
terms_[i] = NewTerm;
}이 때 아무 값이 들어가있지 않을 때도 값을 비교해야하므로 생성자에서 col, row 초기값을 INT_MAX로 잡아준다.
SparseMatrix::SparseMatrix(int num_rows, int num_cols, int capacity)
{
this->num_rows_ = num_rows;
this->num_cols_ = num_cols;
this->capacity_ = capacity;
this->num_terms_ = capacity;
terms_ = new MatrixTerm[this->capacity_];
for (int i = 0; i < this->capacity_; ++i)
{
MatrixTerm Term;
Term.col = INT_MAX; // 중요
Term.row = INT_MAX; // 중요
Term.value = 0;
terms_[i] = Term;
}
}
float SparseMatrix::GetValue(int row, int col) const
{
for (int i = 0; i < num_terms_; ++i)
{
if (row < terms_[i].row) // 원하는 row의 범위를 지나갔음
break;
if (row == terms_[i].row && col == terms_[i].col)
return terms_[i].value;
}
return 0.0f;
}
SparseMatrix SparseMatrix::Transpose()
{
SparseMatrix temp(num_cols_, num_rows_, capacity_); // num_cols_, num_rows_ 순서 주의
for (int i = 0; i < num_terms_; ++i)
temp.SetValue(terms_[i].col, terms_[i].row, terms_[i].value);
return temp;
}
float SparseMatrix::GetValue(int row, int col) const
{
for (int i = 0; i < num_terms_; ++i)
{
if (row < terms_[i].row) // 원하는 row의 범위를 지나갔음
break;
if (row == terms_[i].row && col == terms_[i].col)
return terms_[i].value;
}
return 0.0f;
}
추천구현
Key값 row * num_cols + col은 항상 유일하고 순서대로 정렬할 수 있다.
terms_에 쓰레기 값이 들어있으므로 구현이 되지 않은 index에 접근 불가해야 한다.
따라서 num_cols_는 구현의 핵심이다.
SparseMatrix::SparseMatrix(int num_rows, int num_cols, int capacity)
{
terms_ = new MatrixTerm[capacity];
this->num_rows_ = num_rows;
this->num_cols_ = num_cols;
this->capacity_ = capacity;
this->num_terms_ = 0;
}
num_cols_가 0일 때 SetValue에서 값을 할당해야한다. 따라서 else if(curKey > key) 내부에서 shift를 구현하면 안된다.
num_terms_++
void SparseMatrix::SetValue(int row, int col, float value)
{
if (value == 0.0f) return; // value가 0이 아닌 term만 저장
int key = row * num_cols_ + col;
int i;
for (i = 0; i < num_terms_; ++i)
{
int curKey = terms_[i].row * num_cols_ + terms_[i].col;
if (key == curKey)
{
terms_[i].col = col;
terms_[i].row = row;
terms_[i].value = value;
return;
}
else if (key < curKey)
break;
}
// Shift
num_terms_++;
for (int j = num_terms_ - 1; i < j; --j)
terms_[j] = terms_[j - 1];
terms_[i].col = col;
terms_[i].row = row;
terms_[i].value = value;
}
key 값이 유일하고 정렬되어있으므로 이를 활용할 수 있다.
float SparseMatrix::GetValue(int row, int col) const
{
int key = row * num_cols_ + col;
for (int i = 0; i < num_terms_; ++i)
{
int curKey = terms_[i].row * num_cols_ + terms_[i].col;
if (curKey == key)
return terms_[i].value;
else if (key < curKey)
break;
}
return 0.0f;
}
SparseMatrix SparseMatrix::Transpose()
{
SparseMatrix temp(num_cols_, num_rows_, capacity_); // num_cols_, num_rows_ 순서 주의
// O(num_terms * (num_terms + num_terms))
// = O(num_terms^2)
for (int i = 0; i < num_terms_; ++i)
temp.SetValue(terms_[i].col, terms_[i].row, terms_[i].value);
return temp;
}
참고
1. { }를 활용하여 간단하게 구조체를 정의할 수 있다. 이 때 멤버변수의 순서가 반드시 일치해야 한다.
struct MatrixTerm
{
int row;
int col;
float value;
};
// 1
terms_[i].row = row;
terms_[i].col = col;
terms_[i].value = value;
// 2
terms_[i] = {row, col, value};
2. 동적할당 initialization
https://stackoverflow.com/questions/12694214/initialize-a-float-array-on-construction
더해보기
더하는 두 행렬은 동일한 row과 col을 가지며 capacity = row * col으로 설정하였다.
SparseMatrix SparseMatrix::Add(const SparseMatrix& b)
{
SparseMatrix temp(b.num_rows_, b.num_cols_, b.capacity_);
int cur = 0;
int pram = 0;
while (cur < num_terms_ && pram < b.num_terms_)
{
int curKey = num_cols_ * terms_[cur].row + terms_[cur].col;
int pramKey = b.num_cols_ * b.terms_[pram].row + b.terms_[pram].col;
if (curKey < pramKey)
{
temp.SetValue(terms_[cur].row, terms_[cur].col, terms_[cur].value);
cur++;
}
else if (pramKey < curKey)
{
temp.SetValue(b.terms_[pram].row, b.terms_[pram].col, b.terms_[pram].value);
pram++;
}
else
{
temp.SetValue(terms_[cur].row, terms_[cur].col, terms_[cur].value + b.terms_[pram].value);
cur++;
pram++;
}
}
for (; cur < num_terms_; ++cur)
temp.SetValue(terms_[cur].row, terms_[cur].col, terms_[cur].value);
for (; pram < b.num_terms_; ++pram)
temp.SetValue(b.terms_[pram].row, b.terms_[pram].col, b.terms_[pram].value);
return temp;
}'CS > Data Structure' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [Data Structures] 챕터6. 연결 리스트 (0) | 2023.12.13 |
|---|---|
| [Data Structures] 챕터5. 큐(Queue) (0) | 2023.11.30 |
| [Data Structures] 챕터4. 스택(Stack) (0) | 2023.11.29 |
| [Data Structures] 챕터2. 재귀(Recursion) (0) | 2023.11.27 |
| [Data Structures] 챕터1. 기본개념 (0) | 2023.11.25 |



